How to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
How to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada is an essential financial strategy that can help you maximize savings and minimize tax liabilities. Paying taxes is a part of life, but that doesn’t mean you should pay more than necessary. Canada’s tax system offers various strategies to help individuals lower their taxable income legally. By taking advantage of government-approved deductions, credits, and savings plans, you can keep more of your hard-earned money. Whether you’re saving for retirement, education, or a first home, tax-efficient planning can make a significant difference.
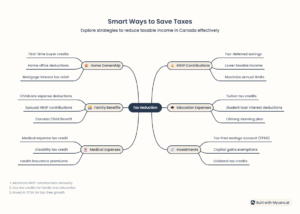
In this guide, we’ll explore practical ways on how to reduce your taxable income in Canada, covering everything from Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSPs) to Pension Income Splitting and key tax credits. Let’s dive in!
1. Smart Accounts to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP)
One of the most effective ways to reduce your taxable income in Canada is by contributing to an RRSP. Contributions to this account are tax-deductible, meaning every dollar you invest reduces your taxable income for that year. Additionally, investments within an RRSP grow tax-free until withdrawal, usually during retirement, when you may be in a lower tax bracket.
Example: If you earn $80,000 per year and contribute $10,000 to your RRSP, your taxable income drops to $70,000, potentially lowering your tax bracket and overall tax burden.
Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA)
Although TFSAs do not offer immediate tax deductions, they allow investments to grow tax-free, making them a valuable tool for long-term savings. Unlike RRSPs, withdrawals from a TFSA are not taxed, making them useful for emergency funds or supplemental retirement income.
First Home Savings Account (FHSA)
The FHSA is designed to help first-time homebuyers save for a down payment. Contributions to an FHSA are tax-deductible, similar to an RRSP, and withdrawals for purchasing a home are tax-free. This dual benefit makes it an excellent tool for reducing taxable income while building toward homeownership.
2. Education-Based Ways on How to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP)
An RESP is a tax-sheltered savings account that helps parents save for their children’s post-secondary education. While contributions themselves are not tax-deductible, investment growth is tax-deferred, and government grants (such as the Canada Education Savings Grant) provide additional incentives.
Lifetime Learning Plan (LLP)
The LLP allows individuals to withdraw money from their RRSP to fund their own or their spouse’s education without triggering immediate tax. This strategy helps working professionals upskill while keeping taxable income lower in the years they are studying.
3. Use Family and Property Strategies to Reduce Taxable Income in Canada
Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP)
The HBP allows first-time homebuyers to withdraw up to $35,000 from their RRSP tax-free to purchase a home. Since RRSP contributions reduce taxable income, this strategy helps individuals save for a home while benefiting from immediate tax reductions.
Child Care Expense Deduction
For parents, child care costs can be a significant expense. The Child Care Expense Deduction allows families to claim eligible expenses, such as daycare or babysitting, which directly reduce taxable income. The lower-income spouse must usually claim this deduction, optimizing family tax savings.
Income Splitting Strategies
While Pension Income Splitting is a well-known strategy, there are other income-splitting methods available. Transferring income to a lower-income spouse, setting up a family trust, or utilizing a Spousal RRSP can significantly lower a household’s overall tax burden.
4. Top Tax Credits to Help Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
Disability Tax Credit (DTC)
The DTC provides tax relief for individuals with disabilities or their supporting family members. If eligible, this non-refundable credit reduces taxable income, easing the financial burden on those facing medical or accessibility-related expenses.
Carrying Charges and Interest Expenses Deduction
Certain investment-related expenses, such as interest on money borrowed for investment purposes or professional advisory fees, may be deducted from taxable income under the Carrying Charges and Interest Expenses Deduction. Investors should track these expenses to ensure they’re optimizing their tax strategy.
Capital Gains and Losses
Managing capital gains effectively can help minimize taxes. If you have capital gains, you can offset them by selling underperforming investments at a loss, a strategy known as tax-loss harvesting. Keeping track of these transactions helps optimize your taxable income.
Charitable Donation Tax Credit
Making charitable donations not only supports good causes but also reduces your taxable income. Canada’s tax system offers generous credits for charitable giving, particularly when donations exceed $200.
Moving Expense Deduction
If you move for work, school, or a business, you may be eligible to deduct reasonable moving expenses. Eligible expenses include transportation, storage, and temporary living costs, reducing taxable income.
Medical Expenses Tax Credit
Many medical expenses, including prescription medications, dental procedures, and mobility aids, are eligible for tax credits. Tracking these expenses ensures you maximize deductions available under the Medical Expenses Tax Credit.
5. Additional Tax Planning Tips on How to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
Tax Brackets and Marginal Tax Rate Awareness
Understanding Canada’s tax brackets can help you plan income distributions strategically. If possible, deferring income to a year when you expect to be in a lower tax bracket can help minimize overall tax liability.
Utilizing Non-Refundable Tax Credits
In addition to the DTC, other non-refundable tax credits like the Canada Employment Amount and Tuition Tax Credit can help lower taxable income.
Recent Tax Law Changes
Staying informed about changes in tax laws ensures that you take full advantage of new deductions and credits. Consulting a tax professional can help keep you updated on potential opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About How to Reduce Your Taxable Income in Canada
Can I claim moving expenses if I switch jobs within the same city?
Only if your new job location is at least 40 kilometers closer to your new home compared to your previous residence.
How much can I contribute to an RRSP each year?
As of 2024, the contribution limit is 18% of your earned income from the previous year, up to a maximum of $31,560.
What qualifies as a medical expense for the tax credit?
Expenses such as dental care, prescription medications, and travel expenses to receive treatment can qualify.
Is there a penalty if I don’t repay the Home Buyers’ Plan?
Yes, if you don’t repay the annual minimum amount, it’s added to your taxable income.
Can both spouses claim the child care expense deduction?
Only the lower-income spouse can usually claim this deduction unless specific exceptions apply.
Conclusion
Reducing your taxable income in Canada is not just about finding loopholes—it’s about making smart financial decisions that align with government-approved tax strategies. Whether you’re contributing to an RRSP, leveraging Pension Income Splitting, or claiming valuable deductions like the DTC, there are numerous ways to keep more of your earnings legally.
To get the most out of these strategies, consider speaking with a financial advisor or tax professional. By planning ahead and making informed decisions, you can significantly lower your tax burden and build long-term wealth.
Start optimizing your tax savings today—your future self will thank you!

